AS4, the message transport protocol, is a more complete version of AS2 and provides enhanced security on service exchanges. Progressively integrated by software publishers into their exchange solutions, the AS4 standard is gaining momentum on a global scale. This article is intended to shed light on the AS4 protocol, its usefulness and its impacts.
The origins of AS4
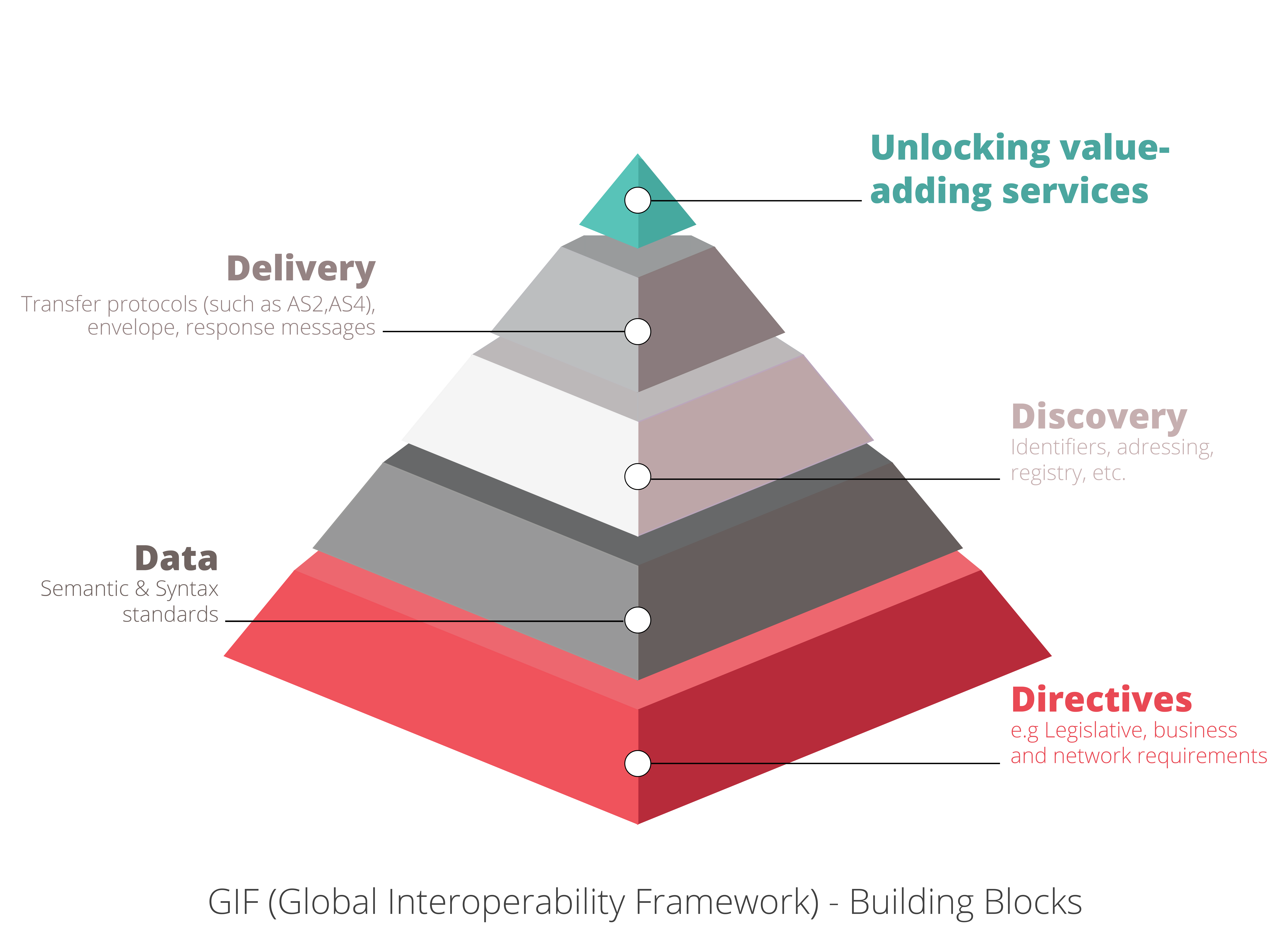
The Global Interoperability Framework (GIF), brings together business associations such as EESPA¹, OpenPeppol², CONNECT ONCE³, and BPC⁴. These associations are working to define recommendations to improve the interoperability of systems for exchanging business information between companies, regardless of the technology, back-office systems and services used by each of them. The aim is to facilitate digital trade, without offering a single global network. To this end, the GIF published an initial summary of its work in June 2020. It is in this context that solution publishers are encouraged to handle used message transport protocols: AS2, and now AS4.
Why AS4 ?
How you integrate your applications and data flows with your suppliers, customers, partners and regulators is more than a mere IT issue. It is also a business issue, critical to order fulfilment, delivery, invoicing and payments.
The public Internet network makes it possible to transport messages from one company to another: the AS2 protocol was developed to provide the necessary security, making it possible to identify that the sender is authorised to exchange with the recipient during a transaction. In addition, encryption services ensure that the messages themselves are well protected. AS2 has therefore naturally become one of the most widely used protocols in the world for exchanging business messages, mainly within EDI solutions. At the same time, more and more web services (Web Services or APIs on the web) are being offered by publishers to enable their solutions to exchange business messages directly from system to system. The publisher develops its web service once, which can then be used by several partners.
More and more web solutions have thus appeared, enabling a company to connect all its partners to the same service. And when this service is offered by Cloud-based solutions used on behalf of their customers, it is understandable that One to One interfaces – cumbersome and expensive – are gradually being replaced by N to N interfaces. For example, an ERP offers a standard Web Service for injecting customer orders for all its customer accounts. This service is then made available to all the company's partners, but also to all customer account partners.
However, Web Services do not have the security strength provided by AS2 when using the Internet network. AS2 has therefore been extended to become AS4, with the aim of providing a security component on service exchanges, as AS2 has done for message exchanges.
With what benefits?
As recalled by the GIF, the use of AS4 is recognised worldwide as the go-to protocol when it comes to service-oriented architectures, based on the http internet transport layer. AS4 allows EDI type exchanges, but also API type exchanges, bringing, among other things, a security aspect.
Each publisher therefore progressively integrates the messages it receives into its own system, making this integration increasingly transparent for its own customers
As you will have understood, the AS4 protocol offers many benefits for your company, your partners and their ecosystem. If you are looking to equip yourself with a B2B automation solution, make sure you choose a vendor that has integrated the AS4 standard into its solution. Whether you have a national or international reach, choosing a solution using the AS4 protocol ensures you simplify your exchanges with your partners, as well as a greater degree of security.
¹European E-Invoicing Service Providers Association
²International association made up of members from the public and private services
³The Open Network for Commerce Exchange, an association focused on development global B2B commerce
⁴The Business Payments Coalition, a global voluntary organisation that aims to promote greater adoption of B2B electronic payments